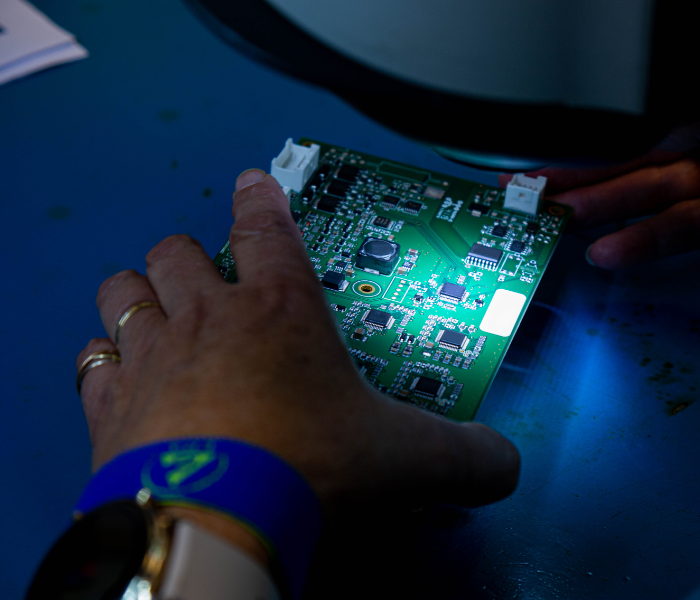
The BMS “Battery Management System” is a term frequently used when talking about batteries, especially those using lithium technology. This electronic card is a fundamental pillar of lithium battery management due to its complexity. It continuously monitors the cells and provides key information about the battery’s condition.
In order to benefit from all the advantages offered by the BMS it is necessary to select the most suitable solution for your lithium battery.
The BMS: 2 main functions
Guaranteeing the safety of the battery
The classic function of the electronic management card is to protect a lithium battery or battery pack from any risks or dangerous circumstances. It provides protection against overvoltage, undervoltage or overcurrent by measuring and monitoring cell temperature, voltage and current.
Some boards have an integrated temperature sensor that allows them to cut off the charge or discharge of the lithium battery, depending on the temperature reading, to prevent thermal runaway, i.e. the degradation of the cells due to intense overheating, which can lead to a battery explosion.
Optimises battery performance over time
Regardless of the electrochemical lithium technology, the BMS ensures that all cells are correctly balanced, i.e. they have the same current intensity and temperature. This function allows it to maximise the capacity of the battery or battery pack and avoid wear and tear in the long term.
Good management of the temperature and balance of the cells by the BMS results in a longer life for the battery.
The different categories of BMS
It is possible to classify the electronic management boards of a lithium battery into 2 categories:
- BMSs with simple functions, commonly called PCMs (Protection Circuit Modules), which provide standard protection against overvoltages, undervoltages and overcurrents with a very basic balancing function for the card’s electronic components;
- Smart BMS or “high level” BMS. In addition to the above functions, they can manage a greater number of configurations (calculate the state of charge and the state of health of the battery, provide self-diagnosis functions, etc.), while potentially communicating with other electronic elements (smart chargers, remote display, etc.).
Among the many differences between these two electronic management cards, the most important one to highlight is the lack of security of PCMs. Indeed, by definition, PCMs are limited in that they only perform a small number of functions to protect the battery or battery pack.
PCMs do not have the software intelligence of Smart BMSs and their microcontrollers to ensure accurate measurement of the battery cell temperature. This means that there is a risk of overheating the cells and therefore of thermal runaway.
The choice of a Smart BMS is therefore recommended to ensure the full safety of a lithium battery or battery pack.
Three questions to ask yourself when choosing your Smart BMS
The choice of a BMS depends mainly on the application in which the battery or lithium battery pack is integrated. Indeed, the electronic card selected for the lithium battery pack of an embedded solutions (e.g. electric vehicle) will not be the same as the one intended for the management of a battery of a stationary application.
Three questions can guide you in the choice of your solution:
What is the maximum current that my battery or battery pack can deliver?
This will allow you to choose the maximum amperage at peak load, particularly for the BMS. Some electronic boards are specially designed for applications that require a lot of power, such as electric vehicles (buses, trucks, powerful vehicles, etc.). Others are more suitable for light applications or those with lower energy peaks (electric bicycles, stationary applications etc).
What is the voltage of my battery?
The higher the voltage required for the battery, the greater the number of cells it will contain. It is therefore important to choose a BMS that is adapted to these key characteristics of the battery.
Do I need to optimise space in my application?
The issue of space optimisation in BMS refers to the notion of the powerbox. As part of the BMS, the powerbox is a set of electronic components that supply energy to the BMS and measure, monitor and control the current flowing through the battery.
Some BMSs have an internal powerbox, i.e. located on the board, while others require an external powerbox. The use of an internal powerbox allows for space optimisation as it does not require an external installation to the BMS.
However, it is important to note that the choice of powerbox is linked to the current intensity that the BMS must handle. For batteries of more than 50A continuous and 100A discharge, the use of an external powerbox is necessary because it is more powerful.
The internal powerbox will therefore be present on BMSs dedicated to small mobility (electric bikes, scooters etc.) or applications requiring little power.
Smart BMS designed by BMS PowerSafe according to your application
As an electronics expert, BMS PowerSafe designs BMSs adapted to each project. We develop the most reliable and efficient solution to ensure the safety of your application while respecting your technical constraints.
Some examples of applications and the customisable PowerSafe BMS electronic board to select from:
- Micro mobility (electric scooters, electric bikes etc) : 10S BMS
- Small mobility (bikes, scooters, small delivery vehicles), stationary applications: 6-18S BMS, 14S BMS
- Robotics: 14S and 6-18S BMS
- Electric vehicles (bus, truck, powerful vehicles etc): High voltage BMS
Would you like to know more about our BMS? Please contact us.